Reference
Lesson 2: Triangle rasterization and back face culling · ssloy/tinyrenderer Wiki — 第 2 课:三角形光栅化和背面剔除 ·ssloy/tinyrenderer 维基 (github.com)
https://www.cnblogs.com/TenosDoIt/p/4024413.html
扫线法绘制面
用扫线法绘制面,就类似于我们画画一样,一条一条线的画,直到将三角形画满。
在上一节课中我们已近写了画线的方法了,需要得到两个点,我们从下往上画,每次都得到三角形两个边上的对应顶点。
就像下面的图形一样:
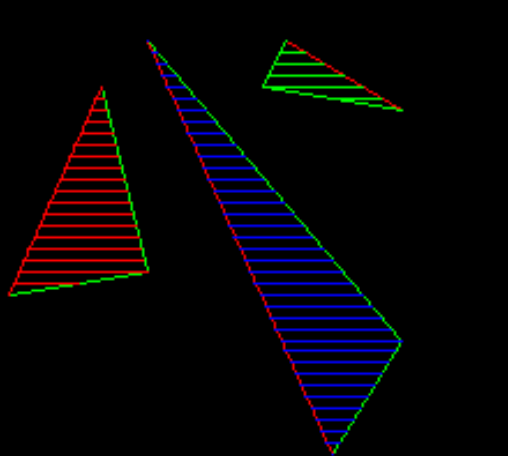
但是有的同学已经发现问题了,这样做的话我们不能一次全部扫完,需要将三角形分为两段。
将高度差最大的边 (V0V2) 找到,并且在高度在中间的点 (V1) 上做一条水平线,得到水平线与高度差最大的边的交点 (Mid),并且以这个交点与高度在中间的点 (V1) 为划分线将三角形划分开。
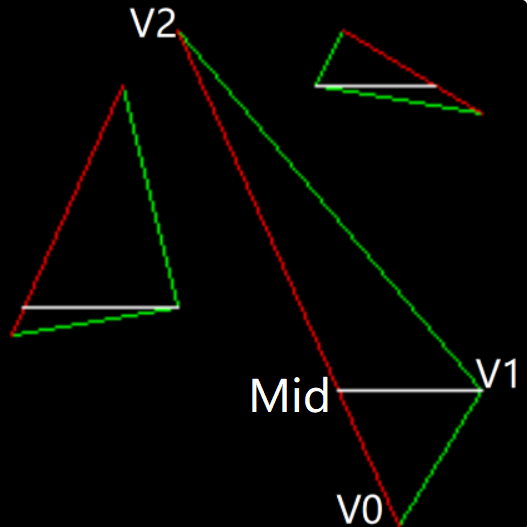
求解的话,用最简单的两点式求解就好了。
1 | int xy_learp(int x0, int y0, float t, int x) { |
t就是斜率,并且根据如果求解y,翻转输入参数x0,y0,并且斜率是原来的倒数,例如:
1 | float t_01 = (float(v1.x - v0.x) / (v1.y - v0.y)); |
下面是源码时间:
1 | //扫线法 |
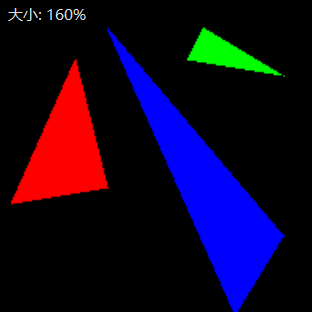
很完美。
包围盒遍历法
这个方法我们先要得到包围这个三角形的矩形,然后遍历这个矩形的像素,判断某个像素点在不在三角形内。
点是否在三角形内
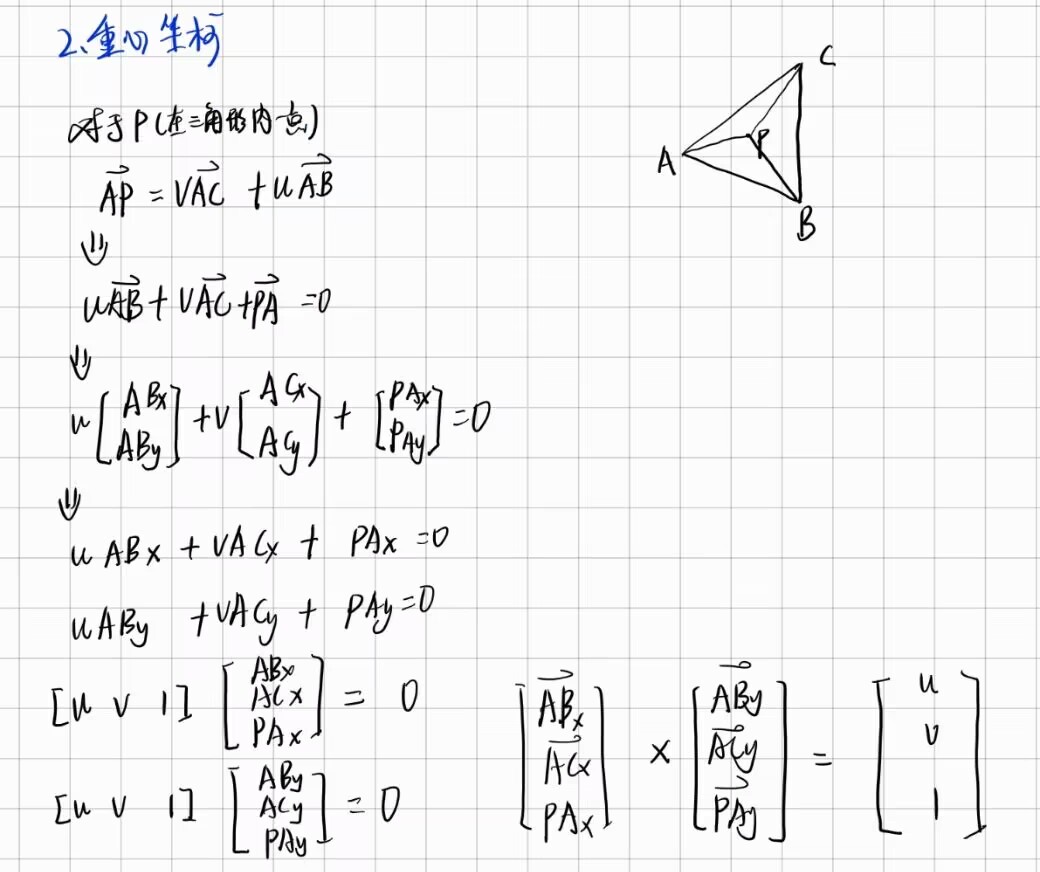
这个求解暂时不知道求对没有,暂且先记下来吧,现在知道了u v w是下面两个叉乘结果
补充:

于是我们得到最关键的函数:
1 | //返回 u v w |
我们找出三角形的包围盒,并且开始遍历,如果像素点在三角形内就上色。
1 | //遍历法 |
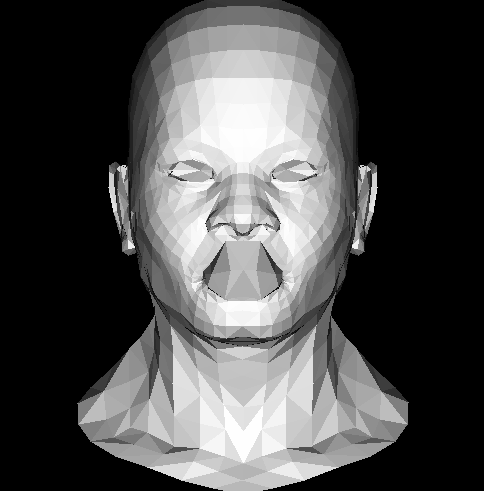
加载模型
现在我们遍历模型的每一个三角形,并且得到每个面的法线(用叉乘得到),并且用光源方向与法线方向做点乘(兰伯特),得到光强,与颜色相乘得到最终颜色,我们去掉为负数的点乘结果,为负数说明光源方向与法线方向大于90度是来自背面的光。
1 | //加载模型面 |

完美。