著作权归作者所由,如有侵权请联系我删除
作者: Deadexow
笑看人间沧海,独活岁月轮转
地址:Navigation Mesh寻路算法 - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
首先这是翻译的是澳大利亚维多利亚大学(Victoria University)由Xiao Cui和Hao Shi两位大佬写的一篇关于Navigation Mesh的算法
Summary Pathfinding is a fundamental problem that most commercial games must deal with. Due to the increase in game complexity, early solutions to the problem of pathfinding were soon overwhelmed. $A^*$ alone, a classic search algorithm, is no longer sufficient to provide the best solution. The popularization of using navigation mesh in pathfinding makes $A^*$ search a very small proportion of pathfinding implementation. In this paper, it systematically reviews the entire process of using a navigation mesh to find an optimal path. First a general pathfinding solution is described. Then examples of using $A^*$ in a navigation mesh are given. Additionally, implementation details of using funnel algorithm in both triangulation and polygonization are given, which is a major contribution of this paper.
Key words Pathfinding, $A^*$, navigation mesh, triangulation, funnel algorithm
摘要: 寻路是大多数商业游戏必须解决的基本问题。由于游戏复杂性的增加,寻路问题的早期解决方案很快就被淘汰。经典搜索算法$A^*$不再是最佳的解决方案。随着寻路中使用导航网格的普及,$A^*$算法在寻路实现中所占比例非常小。本文系统地回顾了使用导航网格寻找最优路径的整个过程。首先描述了一种通用的寻路解决方案。然后给出了在导航网格中使用$A^*$的示例。此外,给出了在三角剖分和多边形剖分中使用漏斗算法的实现细节,这是本文的主要内容。
关键词: 寻路,$A^*$,导航网格,三角测量,漏斗算法
**1.Introduction
**For most commercial games, especially real-time strategy games, gameplay experience heavily relies on a brilliant artificial intelligent system. Pathfinding, as a fundamental part of artificial intelligence, is critical to the success of a game. In this multi-billion-dollar industry, game designers have put enormous amount of efforts to improve the pathfinding performance. As a computational intensive task, pathfinding often requires huge amount of computational resources. However, in practice, the major part of these resources is allocated to graphics. Because only limited CPU time and memory space are available, itis very important to improve efficiency of a pathfinding solution
对于大多数商业游戏,尤其是即时战略游戏,游戏体验严重依赖于优秀的人工智能系统。寻路,作为人工智能的基础部分,对游戏的成功至关重要。在这个数十亿美元的游戏产业中,游戏设计者投入了巨大的努力来提高寻路性能。作为一项密集计算的程序,寻路通常需要大量的计算资源。然而实际上,这些资源_[指计算机计算资源]的主要部分是分配给图形的[即图像处理]_。因为只有有限的CPU时间和内存空间可用,所以提高寻路解决方案的效率非常重要。
Navigation mesh is a technique to represent a game world using polygons. Due to its simplicity and high efficiency in representing the 3D environment, navigation mesh has become a mainstream choice for 3D games. According to the number of sides of polygons, navigation mesh can be categorized into triangulation and polygonization.Implementation details of using funnel algorithm in both of them are given. A general pathfinding solution is described in Section 3 and intuitive examples of pathfinding in both triangulation and polygonization are given in Section 4.
导航网格是一种使用多边形来表示游戏世界_[游戏可行走区域]_的技术。由于其在表现3D环境方面的简单性和高效性,导航网格已经成为3D游戏的主流选择。根据多边形的边数,导航网格可以分为三角网和多边形网。给出了在两者中使用漏斗算法的实现细节。第3节描述了一般的寻路解决方案,第4节给出了三角剖分和多边形剖分中的直观寻路示例。
**2.Pathfinding
**Generally speaking, pathfinding is a process of determining a set of movements for an object from one position to another, without colliding with any obstacles in its path. Obviously, selecting a reasonable path for each moving object is often considered the most fundamental artificial intelligence task in a commercial game.
一般来说,寻路是确定物体从一个位置到另一个位置的一组运动的过程,在其路径上不与任何障碍物碰撞。显然,为每个移动的对象选择合理的路径通常被认为是商业游戏中最基本的人工智能任务。
A ‘reasonable’ path must have two properties. The first property is called validity which is the most common measure to indicate whether or not the path is collision free. The second property is called optimality which is measured normally by either a distance metric or the time required for travelling through the path. Using a distance metric, an optimal path is simply the shortest path. It means the distance between start and goal in such a path is no greater than any other routes. It is an intuitive requirement. For example, if someone travels from London to Pairs, a route passing through New York would not be considered optimal.
一个“合理的”路径必须有两个属性。第一个属性叫做有效性,这是表示路径是否无冲突的最常见的度量。第二个属性称为最优性,通常通过距离度量或通过路径所需的时间来衡量。使用距离度量,最佳路径就是最短路径。这意味着在这样的路径中,起点和目标之间的距离不比任何其他路线大。这是一种直觉要求。例如,如果某人从伦敦旅行到巴黎,经过纽约的路线不会被认为是最佳的。
Time is another widely used measure. It defines an optimal path as the fastest route. Simply it means the time required for an optimal path to be travelled through is always less than any other routes. In most cases, the shortest path is often the fastest one. . However, there are some special cases. For example, when travelling between two locations, the travel time for following a highway is obviously less than it for driving on a rough road even the distance may be shorter. In the context of commercial games, measuring optimality by time is a better choice, especially in real-time strategy games such as StarCraft and Age of Empires, where the time to reach a destination is more important than the distance travelled
时间是另一种广泛使用的测量方法。它将最佳路径定义为最快的路线。简单地说,这意味着一条最佳路径所需的时间总是比其他任何路线都要少。在大多数情况下,最短的路径往往是最快的路径。但是,也有一些特殊情况。例如,当在两个地点之间行驶时,沿公路行驶的时间明显少于在崎岖道路上行驶的时间,即使距离可能更短。在商业游戏的环境中,用时间来衡量最优性是一个更好的选择,特别是在即时战略游戏中,如星际争霸和帝国时代,到达目的地的时间比旅行的距离更重要。
Regarding efficiency of a pathfinding solution, generally it is measured by execution time and memory usage. According to existing research, finding a nearly optimal path only requires a small part of the resources that are needed to find an exactly optimal path. As commercial games often impose strict requirements on both execution time and memory usage, finding an exactly optimal path is not always worthwhile. As long as the path appears ‘reasonable’, a suboptimal approach is usually acceptable.
关于寻路解决方案的效率,通常通过执行时间和内存使用来衡量。根据现有的研究,找到接近最优的路径只需要找到精确最优路径所需的一小部分资源。由于商业游戏通常对执行时间和内存使用都有严格的要求,因此寻找一条完全最优的路径并不总是值得的。只要路径看起来“合理”,次优方法通常也是可以接受的。
3. Approach to pathfinding
Generally speaking, finding an optimal path for a game character requires at least 3 stages. At the 1st stage, a game world is transformed into a geometric representation such as a navigation mesh. There are many ways to approachbut they are not discussed in this paper. Once a navigation mesh is generated, no matter it is a triangulation or a polygonization, at stage 2 $A^*$ search is performed in such amesh. Because $A^*$ search could not give a real path (see Section 4.1 for detail), further processes are required to find a real path, which is the 3rd stage. A popular algorithm, simple stupid funnel algorithm, is used to overcome the issue. Demonstrations of the simple stupid funnel algorithm in both triangulation and polygonization are given in Section 4.2 and Section 4.3 respectively.
一般来说,找到一个游戏角色的最佳路径至少需要3个阶段。在第一阶段,游戏世界被转换成几何表示,例如导航网格。有许多方法可以达到这一目的,但本文不做讨论。一旦生成了导航网格,不管它是三角剖分还是多边形化,在阶段2,在这样的网格中执行$A^*$搜索。因为$A^*$搜索不能给出真实路径(详见第4.1节),所以需要进一步的过程来找到真实路径,这是第三阶段。一个流行的算法,简单愚蠢的漏斗算法,是用来克服这个问题。在4.2节和4.3节中分别给出了三角剖分和多边形化中的简单愚蠢漏斗算法的演示。
4. Navigation Mesh
Navigation Mesh (NavMesh) is a method for representing a game world using polygons. Polygons on a NavMesh must be convex. The properties of a convex polygon could guarantee a free-walk for a game character as long as such a character stays in the same polygon [1]. Triangulation is a special case of NavMesh as all of its polygons on the NavMesh are triangles. In most cases, the number of sides of polygons on a NavMesh varies from 3 to 6; as in practice, over 6 could result in a significant increase in memory usage [2].
导航网格(NavMesh)是一种使用多边形来表示游戏世界的方法。NavMesh上的多边形必须是凸的。凸多边形的性质可以保证一个游戏角色的自由行走,只要这样一个角色停留在同一个多边形内。三角剖分是NavMesh的特例,因为它在NavMesh上的所有多边形都是三角形。在大多数情况下,NavMesh上多边形的边数从3到6不等;实际上,边数超过6可能会导致内存使用的显著增加。
4.1 $A^*$ in a NavMesh
Below is a brief example of how $A^*$ works in a NavMesh. Let G be a graph with P polygons which are walkable and B polygons which are blocked as shown in Fig. 1.
下面是一个简单的例子,说明$A^*$在NavMesh中是如何工作的。设G是一个图,其中P个多边形是可走的,B个多边形是封闭的,如图1所示。
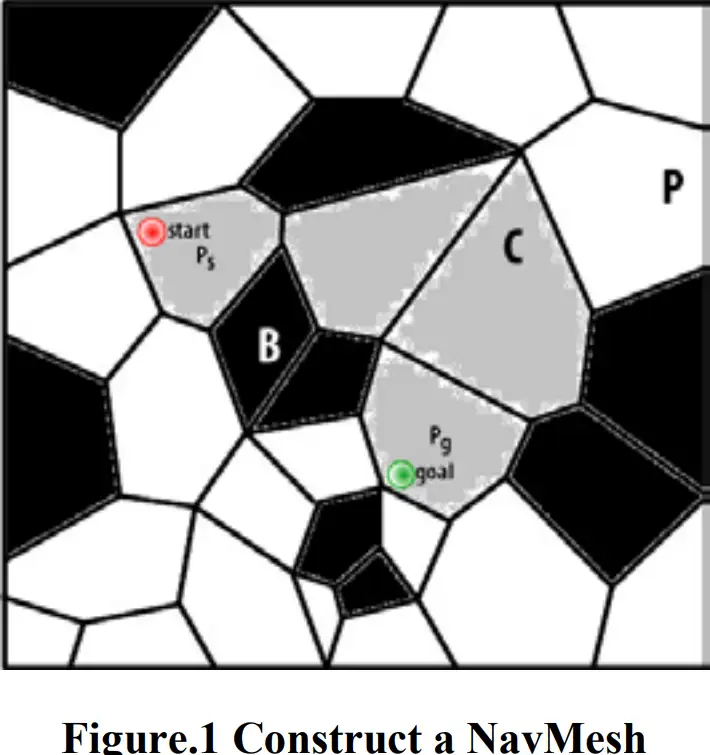
First, we must find a set of polygons ⊆ where an optimal path will go through. If Ps is the polygon where the start is, then Ps must be the first polygon in C. If Pg is the polygon where the goal is, then Pg must be the last polygon in C. To find the remaining parts of C, we must make some changes in the map. Each polygon in G is mapped to a node in G’. For instance, Ps is mapped to Nsand Pg is mapped to Ng. Each edge shared by two polygons in G is mapped to an edge connecting two nodes in G’ as shown in Fig. 2
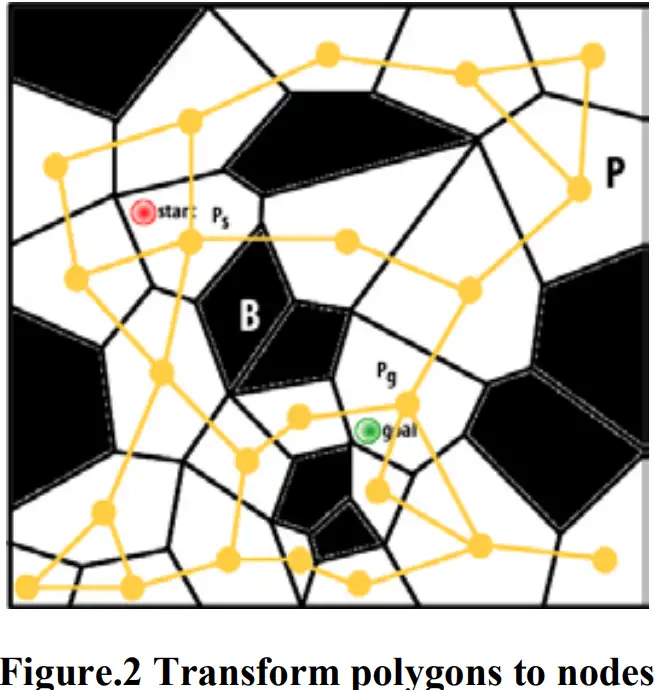
首先,我们必须找到一组多边形 ⊆ ,一个最佳路径将通过。如果Ps是起点所在的多边形,那么Ps一定是C中的第一个多边形,如果Pg是目标所在的多边形,那么Pg一定是C中的最后一个多边形,要找到C的剩余部分,我们必须在地图中做一些改变。G中的每个多边形映射到G ‘中的一个节点。例如,Ps映射到NSA,Pg映射到Ng。如图2所示,G中两个多边形共享的每条边被映射到连接G’中两个节点的边。
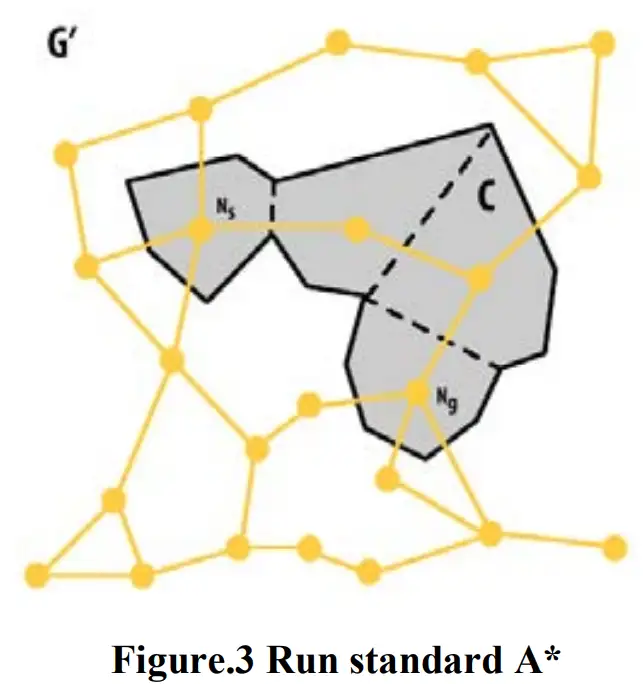
Then, an optimal path p from Ns to Ng in G’ can be found with $A^*$. As each node in G’ corresponds to a polygon in G, each node in p corresponds to a polygon in C as shown in Fig. 3.
然后,在G’中从Ns到Ng的最优路径p可以用$A^*$找到。由于G’中的每个节点对应于G中的一个多边形,所以p中的每个节点对应于C中的一个多边形,如图3所示。
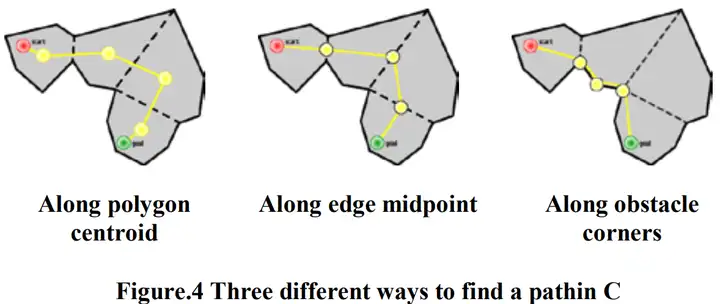
C is not a real path; instead, it is a set of polygons. Fig. 4 illustrates three different ways to find a real path in C. No matter which method we use, none of them could guarantee an optimal path. Thus, further process is required.
C不是真正的路径;相反,它是一组多边形。图4 说明了在C中寻找真实路径的三种不同方法 不管我们用哪种方法,他们都不能保证最佳路径。因此,更进一步的过程是必需的。
4.2 Triangulation
Triangulation is a special case of NavMesh where polygons are replaced with triangles. The minimum angle of a triangle must be maximized. This property guarantees an optimal path will not cross any triangle more than once [3]. Using $A^*$ alone could not yield a real path in a triangulation; instead, a set of triangles with a start and a goal is given. A channel is formed, a simple polygon with start and goal as two nodes and which traces perimeter of triangles in between as shown in Fig. 5. We aim to find a real path within it to use for object motion.
三角剖分是NavMesh的一种特殊情况,其中多边形被替换为三角形。三角形的最小角必须最大化。这一特性保证了最佳路径不会与任何三角形交叉超过一次。在三角测量中,单独使用$A^*$不能产生真正的路径,而是给出一组有起点和终点的三角形。在形成的路径中,一个以起点和终点为两个节点的简单多边形描绘了中间三角形的周长,如图5所示。而我们的目的就是在其中找到一条真实的路径用于物体运动。
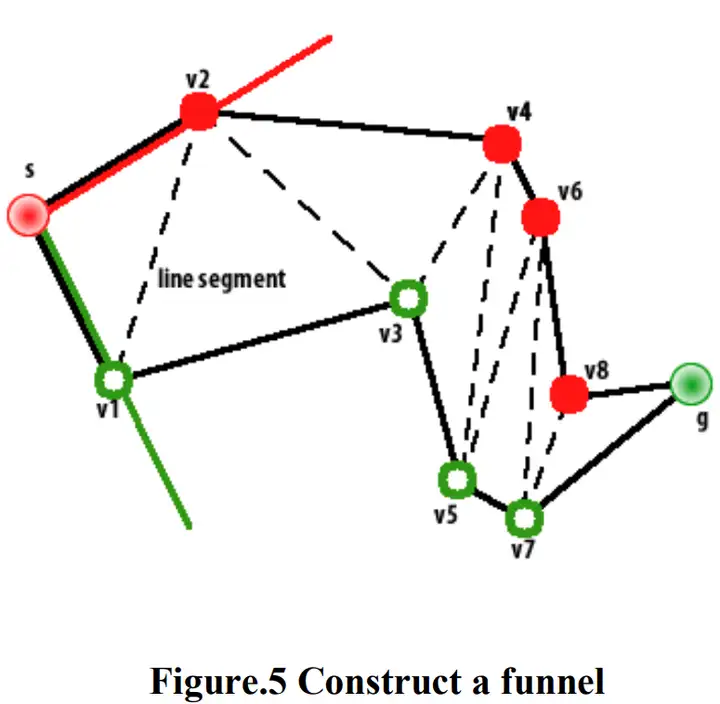
For a point object, such path could be found with funnel algorithm in linear time. Instead of describing the original funnel algorithm, here we prefer to present a simplified version, simple stupid funnel algorithm (SSF)which was first time introduced by Mononen in 2010.
对于一个点目标,这种路径可以用漏斗算法在线性时间内找到。在这里,我们不描述原始的漏斗算法,而是更愿意给出一个简化的版本,简单愚蠢的漏斗算法(SSF),它是由Mononen在2010年首次提出的。
For example, as shown in Fig. 5, a channel is formed from 8 triangles with 7 line segments. A funnel is constructed using the node s (s represents the start) and the endpoints (v1and v2) of the first line segment (from left to right). [sv2] epresents the left funnel edge and [sv1] represents the right funnel edge. Assume v2 is the left node and v1 is the right node. Then, the next left and right nodes are v2 and v3respectively. The rest could be done in the same manner. [1]
例如,如图5所示,路径由具有7条线段的8个三角形形成。使用第一条线段(从左到右)的节点s (s代表起点)和端点(v1和v2)构建漏斗。sv2代表左漏斗边缘,sv1代表右漏斗边缘。假设v2是左节点,v1是右节点。然后,下一个左右节点分别是v2和v3。其余的可以用同样的方式完成。
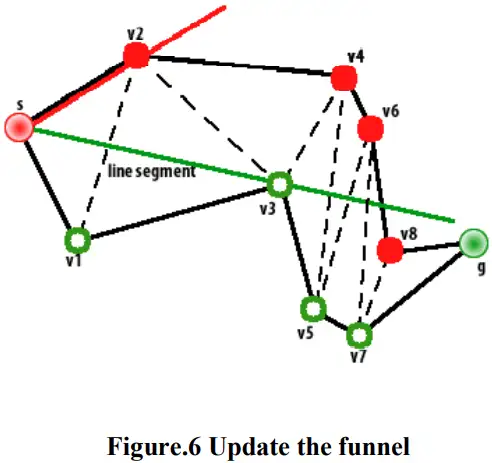
All of the left nodes are represented by solid circles and all of the right nodes are represented by hollow circles. If the next left and right nodes are inside the funnel, for instance as shown in Fig. 5, v2 and v3 are both inside the funnel, simply narrow the funnel as shown in Fig. 6. If the next left node is outside the funnel, do not update the funnel.
所有左侧节点由实心圆表示,所有右侧节点由空心圆表示。如果接下来的左节点和右节点在漏斗内,例如如图5所示,v2和v3都在漏斗内,则简单地缩小漏斗,如图6所示。如果左下一个节点在漏斗之外,则不要更新漏斗。
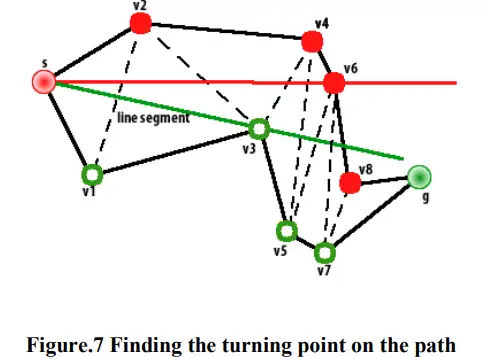
If the next left node is over the right funnel edge, for instance as shown in Fig. 7, v8 is over the right edge, set v3 as an apex in the path and construct a new funnel using v3, v4 and v5 and restart the above steps as shown in Fig. 8
如果下一个左节点在右漏斗边缘之上,例如如图7所示,v8在右边缘之上,则将v3设置为路径中的顶点,并使用v3、v4和v5构建新的漏斗,并如图8所示重新开始上述步骤
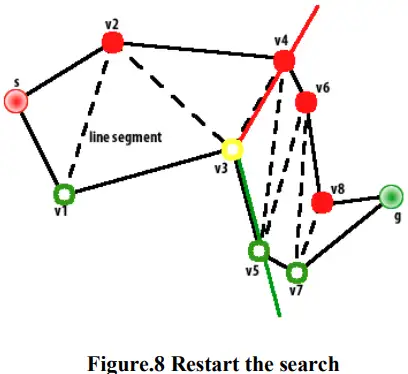
The same logic goes for right nodes as well. These steps are repeated until all the line segments are processed. Then, a shortest path from s to g is found. Instead of using a double-ended queue in the original funnel algorithm, SSF runs a loop and restarts the loop from earlier location when new apex is added. Some line segments may be calculated more often than others because of the restart, but the calculations are too simple to impair the execution time. This simplified version is much easier to implement and in practice is even faster as well. Compared with the original funnel algorithm where a triangulation is required, SSF provides the possibility to be deployed in a polygonization.
同样的逻辑也适用于右节点。重复这些步骤,直到处理完所有线段。然后,找到从s到g的最短路径。SSF没有在最初的漏斗算法中使用双端队列,而是运行一个循环,并在添加新的尖端节点从先前的位置重新开始循环。由于重新运算时,一些线段可能比其他线段计算得更频繁,但是计算太简单而不会影响执行时间。这个简化的版本更容易实现,实际上也更快。与需要三角剖分的原始漏斗算法相比,SSF提供了部署在多边形化中的可能性。
4.3Polygonization
If a NavMesh is not a triangulation, it must be a polygonization. Such a NavMesh must have a property of at least one of its polygons that the number of sides is greater than 3. All polygons on a NavMesh must be convex. This property guarantees a game character could move anywhere it likes to in a straight line as long as it stays in the same polygon. $A^*$ alone could not generate a real path as stated before; instead, a series of polygons are given. Similar with pathfinding in a triangulation, SSF can be used to find a real path in the channel. As described in Section 4.2, apexes can be found by analyzing the relative position between nodes and edges. Thus, being able to identify the left or right nodes correctly is critical to SSF.
如果一个NavMesh不是三角剖分,那么它一定是多边形化。这样一个NavMesh必须至少有一个多边形的边数大于3。NavMesh上的所有多边形都必须是凸的。这个属性保证了游戏角色可以沿着直线移动到它想要去的任何地方,只要它停留在同一个多边形中。如前所述,单独的$A^*$不能生成真实路径;而是给出一系列多边形。与三角测量中的寻路类似,SSF可用于寻找信道中的真实路径。如4.2节所述,顶点可以通过分析节点和边之间的相对位置来找到。因此,能够正确识别左侧或右侧节点对SSF至关重要。
In a triangulation, the left and right nodes can be easily found. For example, as shown in Fig. 5, v3 is a right node because v2 is a left node which is set at the beginning. As v3 is a right node, v4, another endpoint in the same line segment with v3, must be a left node. However, in a polygonization, it is slightly different. In a polygonization, as long as the vertices in the polygons are stored in a counter clockwise (CCW) order, the first vertex on the line segment is always the right node and the second vertex, another endpoint on the same line segment, is always the left node.
在三角测量中,左右节点很容易找到。例如,如图5所示,v3是右节点,因为v2是在开始时设置的左节点。由于v3是右节点,与v3在同一线段上的另一个端点v4必然是左节点。然而,在多边形化中,情况略有不同。在多边形化中,只要多边形中的顶点以逆时针(CCW)顺序存储,线段上的第一个顶点总是右节点,第二个顶点(同一线段上的另一个端点)总是左节点。
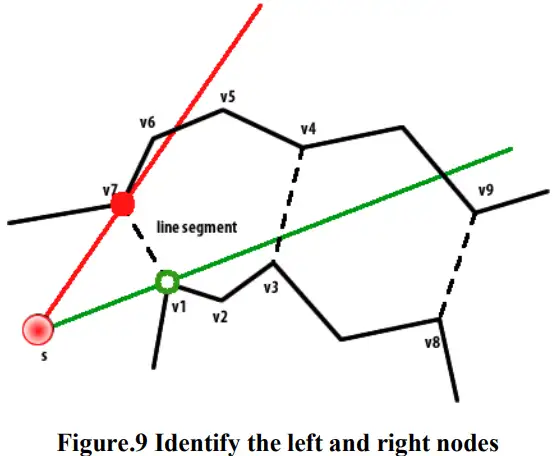
The difference is as shown in Fig. 9, setting v2 is the left node and v1 is the right node. Then, the endpoints v3 and v4 on the second line segment are the right and left nodes respectively. Once the next left and right nodes are identified, the remaining steps are exactly the same as SSF in a triangulation, where the relative positions between the left and right nodes and the funnel edges are used to identify the apexes on the optimal path.
区别如图9所示,设置v2为左节点,v1为右节点。那么,第二条线段上的端点v3和v4分别是右节点和左节点。一旦确定了下一个左右节点,剩下的步骤与三角测量中的SSF完全相同,其中左右节点与漏斗边之间的相对位置用于确定最佳路径上的顶点。
A polygonization provides a possibility to use fewer large polygons to represent a game world. Especially, in real-time strategy games, large open areas are everywhere. In this case, a large polygon could cover the whole open area while a triangle could not able to cope due to its geometric properties. Regarding efficiency, using fewer large polygons could reduce both memory footprint and search space, especially the reduction in the search space could significantly speed up the search.
多边形化提供了使用较少的大多边形来表示游戏世界的可能性。尤其是在即时战略游戏中,大片开阔地随处可见。在这种情况下,一个大的多边形可以覆盖整个开放区域,而一个三角形由于其几何属性而无法应付。关于效率,使用较少的大多边形可以减少内存占用和搜索空间,特别是搜索空间的减少可以显著加快搜索速度。
**5. Conclusion
*This paper reviewed a general approach to finding an optimal path in a navigation mesh and illustrated how to achieve it in both triangulation and polygonization. The solution described in this paper is an $A^$ search with funneling based on a navigation mesh. Although SSF is applicable to both of triangulation and polygonization, a further modification is required when identifying the left and right nodes in a polygonization. A major contribution of this paper is to give implementation details of both of them in an intuitive way. Further work is required to explore applicability of both of triangulation and polygonization to classic game maps as well as compare their performances.
本文回顾了在导航网格中寻找最优路径的一般方法,并举例说明了如何在三角剖分和多边形剖分中实现最优路径。本文描述的解决方案是基于导航网格的漏斗$A^*$搜索。尽管SSF适用于三角剖分和多边形化,但在确定多边形化中的左右节点时,还需要进一步的修改。本文的主要贡献是以直观的方式给出了两者的实现细节。进一步的工作需要探索三角测量和多边形化对经典游戏地图的适用性,以及比较它们的性能。
暂时先写到这里,接下来会搞鬼事的(也就是公开代码)